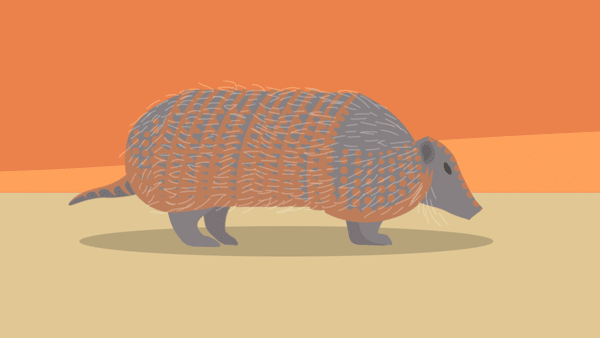
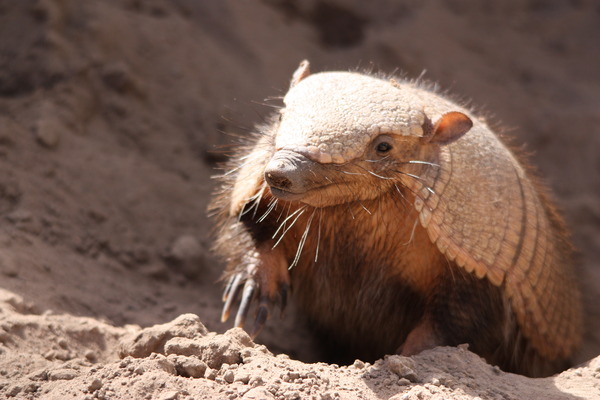
Large hairy armadillo
Chaetophractus villosus
Reproduction: Usually two, but sometimes one or three offspring per litter. Breeds between the end of winter and beginning of spring.
Weight: 2–5 kg
Diet: Mainly beetle adults and larvae, and sometimes plant material (especially fruits), small vertebrates, bird eggs, and carrion.

Common Names
English – Large Hairy Armadillo, Big Hairy Armadillo
Spanish – Peludo, Quirquincho Grande, Tatú Pecho Amarillo
German – Braunborsten-Gürteltier, Braunes Borstengürteltier, Braunhaargürteltier
French – Grand Tatou Velu
Portuguese – Tatu-Peludo
How to Identify:
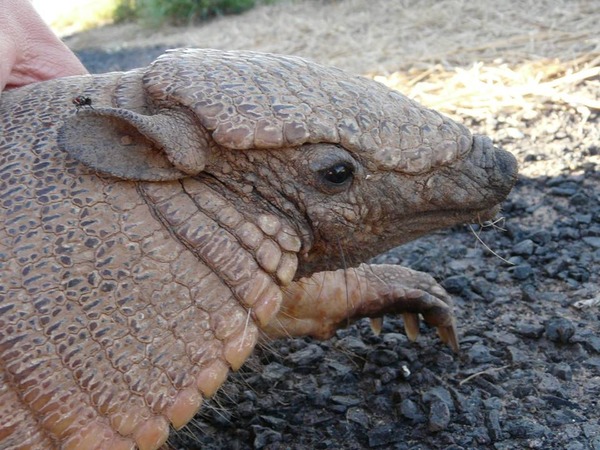
Carapace Flattened Dark Long, thin dark hair Moveable bands 6-7 Ears 3 cm, proportionally short Tail 12–15 cm
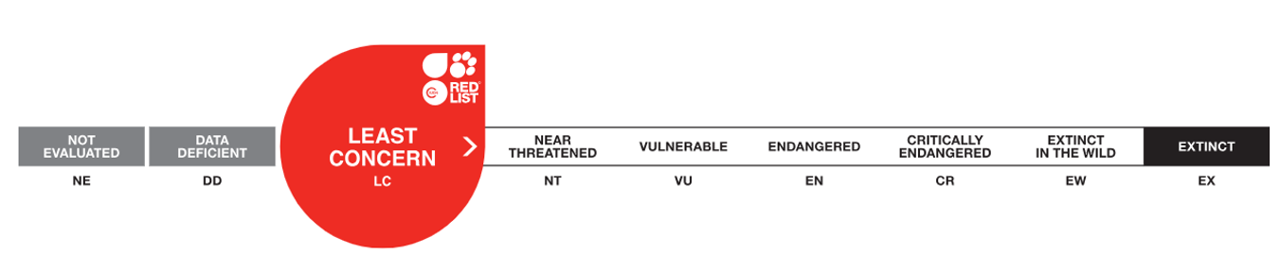
IUCN Red List
Species are classified into one of nine Red List Categories: Extinct, Extinct in the Wild, Critically Endangered, Endangered, Vulnerable, Near Threatened, Least Concern, Data Deficient and Not Evaluated. Vulnerable, Endangered and Critically Endangered species are considered to be threatened with extinction.
Large hairy armadillo Facts
- Its carapace is used, among others, to make charangos, a musical instrument
- One of the few armadillo species that benefits from human activities; it can be quite abundant in agricultural fields
- This species commonly uses man-made landfills and composting sites.
- It has been introduced in Tierra del Fuego, the southernmost tip of South America, where it is considered an invasive species.
- Although usually solitary, up to 10-20 individuals can coexist under certain circumstances, e.g. when food is abundant or during flooding season.
Habitat
- Agricultural areas
- Desert
- Grassland
- Pastures
- Savanna
- Shrubland
 Population Trend
Population Trend
• Stable
 Threats
Threats
• Dogs
• Hunted
• Road accidents
Here are some ways YOU can help keep armadillos healthy and safe:
– It is best to observe them from a distance and in silence.
– Our pets could attack them. It is important to keep your dog on a leash when you go for a walk, or keep your pets at home in an enclosed and safe area. In addition, taking care of our pets also means spaying and neutering them so that they do not breed without control.
– Another way to help protect the areas where armadillos live is by not starting fires.
– Armadillos love to live in nature, keeping them as pets is not good for them. Keep in mind that they don’t like selfies either.
– If you find an injured armadillo, contact a wildlife hospital so they can help it.
– Deforestation is often caused to make more land for livestock. Eating less meat may help save our forests.
Test your new knowledge!
Test your new armadillo expertise by visiting our armadillo word search, puzzles, coloring sheets and name games!
Check out this video to see how much you have learned!
The Anteater, Sloth, Armadillo Specialist Group has a store that directly helps xenarthran conservation!



 Population Trend
Population Trend Threats
Threats